The use of tissue and cell-based medical treatments is rising in both number and frequency thanks to significant advances in biotechnology.
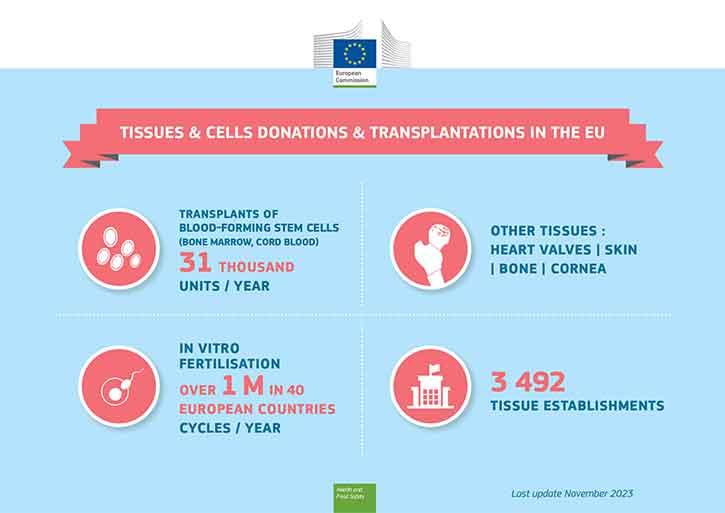
Blood-forming stem cells are transplanted from bone marrow donors (or cord blood) to patients with blood cancer, and/whereas gametes are used for in vitro fertilisation (IVF). Both are well known medical therapies that use human cells. Other invaluable uses of human tissues include skin grafting for burn victims, or corneal grafting to restore sight.
Bone marrow (haematopoietic stem cells) and gametes (sperm, egg cells) for IVF can be donated by living donors, while replacement tissues (like skin, bone, cornea or heart valves) can be donated after death.
The European Commission provides funding for Actions in the area of SoHO mainly in the form of projects or joint actions with national authorities. Actions aim at supporting the EU mandate on safety and quality, but can also serve to promote other policy priorities, such as improving the availability of SOHO or the efficiency of the health systems that support donation and supply.
Legislation
The legal framework defining the safety and quality standards for tissues and cells is set out in Directive 2004/23/EC, also referred to as the European Tissues and Cells Directive, adopted in 2004 by the European Parliament and Council. It covers all steps in the transplant process from donation, over procurement, testing, processing, preservation, storage to distribution.
To help implement this basic act, the Commission proposed and adopted, in close collaboration with EU countries, the following implementing Directives:
- Commission Directive 2006/17/EC regarding certain technical requirements for the donation, procurement and testing of human tissues and cells
- Commission Directive 2006/86/EC concerning traceability requirements, notification of serious adverse reactions and events, additional technical requirements for the coding, processing, preservation, storage and distribution of human tissues and cells
- Commission Directive 2015/565 amending Directive 2006/86/EC as regards certain technical requirements for the coding of human tissues and cells
- Commission Directive 2015/566 implementing Directive 2004/23/EC concerns the procedures for verifying the equivalent standards of quality and safety of imported tissues and cells
Commission Decisions 2010/453/EC and Commission Directive 2012/39/EU, as well as Commission Decision C(2015) 4460 address some further specific aspects.
It is important to note that EU countries can always choose to apply more stringent rules to the quality and safety of tissues and cells then the ones outlined above.
Following an evaluation of the EU legislation on blood and tissues and cells, published in 2019, the Commission has proposed a revision of this legislation which was adopted on 14 July 2022.
Coordination
National competent authorities are responsible for the implementation of the requirements established in EU legislation. The European Commission holds regular meetings with them to facilitate communication, to exchange best practices, and to reach a common understanding on the implementation of the Directives. Periodic surveys, completed by the competent authorities, allow the Commission to draft reports on the implementation of the legislation.






